Table Of Content
Doors in series shall swing either in the same direction or away from the space between the doors. The minimum space between two hinged or pivoted doors in series shall be 48 in (1220 mm) plus the width of any door swinging into the space. Doors in series shall swing either in the same direction or away from the space between the doors (see Fig. 26).
Chapter 7: Communication Elements and Features

The full text of the 2010 Standards is available for public review on the ADA Home Page and on the Access Board’s Web site (last visited June 24, 2010). The Access Board site also includes an extensive discussion of the development of the 2004 ADA/ABA Guidelines, and a detailed comparison of the 1991 Standards, the ADA/ABA Guidelines, and the 2003 International Building Code. The Department has assembled an official online version of the 2010 Standards to bring together the information in one easy-to-access location. It provides the scoping and technical requirements for new construction and alterations resulting from the adoption of revised 2010 Standards in the final rules for Title II (28 CFR part 35) and Title III (28 CFR part 36).
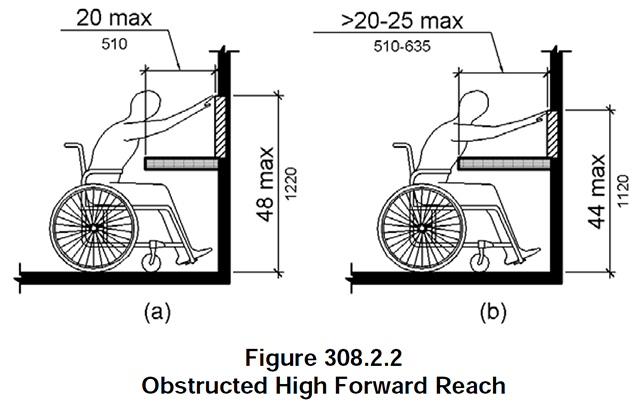
Knee and Toe Clearance
One commenter stated that, in its view, the residential facilities standards were congruent with overlapping requirements from HUD, and that access provided by the residential facilities requirements within alterations would ensure dispersion of accessible features more effectively. This commenter also argued that while the increased number of required accessible units for residential facilities as compared to transient lodging may increase the cost of construction or alteration, this cost would be offset by a reduced need to adapt rooms later if the demand for accessible rooms exceeds the supply. The commenter also encouraged the Department to impose a visitability (accessible doorways and necessary clear floor space for turning radius) requirement for both the residential facilities and transient lodging requirements to allow students with mobilityimpairments to interact and socialize in a fully integrated fashion. The ADA does not exempt spaces because of a belief or policy that excludes persons with disabilities from certain work.
Designing Accessible Laboratory Executive and Continuing Professional Education - HSPH News
Designing Accessible Laboratory Executive and Continuing Professional Education.
Posted: Mon, 14 Jun 2021 07:00:00 GMT [source]
State and Local Accessibility Regulations
Paragraph (b)(2) lists examples of aids and services for making visually delivered materials accessible to persons with visual impairments. Many commenters proposed additional examples such as signage or mapping, audio description services, secondary auditory programs (SAP), telebraillers, and reading machines. While the Department declines to add these items to the list in the regulation, they may be considered appropriate auxiliary aids and services.
A4.2 Space Allowances and Reach Ranges
Where glazed openings are provided in accessible rooms or spaces for operation by occupants, at least one opening shall comply with 309. Each glazed opening required by an administrative authority to be operable shall comply with 309. Dining surfaces and work surfaces required to comply with 902 shall be dispersed throughout the space or facility containing dining surfaces and work surfaces.
The Department is persuaded by the concerns raised by commenters for both the title II and III regulations that the six-month compliance date proposed in the NPRM for application of the Standards may be too short for certain projects that are already in the midst of the design and permitting process. The Department has determined that for new construction and alterations, compliance with the 2010 Standards will not be required until 18 months from the date the final rule is published. Until the time compliance with the 2010 Standards is required, public entities will have the option of complying with the 2010 Standards, the UFAS, or the Standards. However, public entities that choose to comply with the Standards in lieu of the 1991 Standards or UFAS prior to the compliance date described in this rule must choose one of the three standards, and may not rely on some of the requirements contained in one standard and some of the requirements contained in the other standards.
The incremental scoping for wheelchair spaces and companion seats required in assembly areas with fixed seating has been reduced. Under the 1991 Standards, incremental scoping for assembly facilities with more than 500 seats was one additional wheelchair space and companion seat for each increase of 100 seats. Under the 2010 Standards, facilities with 501 to 5000 seats must provide one additional wheelchair space for each additional 150 seats (or fraction thereof) and facilities with more than 5001 seats must one additional space for each 200 seats over 5001. Some provisions in the ADA Standards specify a minimum number of elements or spaces as a minimum percentage or proportion.
7 Curb Ramps
A minimum 132 inch (3350 mm) wide vehicle space is shown with a minimum 60 inch (1525 mm) marked access aisle. Two minimum 132 inch wide (2440 mm) vehicle spaces sharing a 60 inch (1525 mm) minimum width access aisle take up a minimum of 324 inches (8225 mm). People who have difficulty walking or maintaining balance or who use crutches, canes, or walkers, and those with restricted gaits are particularly sensitive to slipping and tripping hazards. For such people, a stable and regular surface is necessary for safe walking, particularly on stairs.
Medical Care and Long-Term Care Facilities
A turning space complying with 304.2 and 304.3 shall be provided in load and unload areas. Where installed in wet locations, the surface of the seat shall be slip resistant and shall not accumulate water. At least 50 percent of shelf space in storage facilities shall comply with 811.
Some commenters noted that persons with disabilities may be required to travel long distances when the locations for examinations for individuals with disabilities are limited, for example, to only one city in a State instead of a variety of cities. The Department has therefore revised this paragraph to add a requirement that such examinations be offered at locations that are as convenient as the location of other examinations. In the final rule, Sec.36.305(c) provides specific requirements regarding alternatives to barrier removal in multiscreen cinemas. In some situations, it may not be readily achievable to remove enough barriers to provide access to all of the theaters of a multiscreen cinema. If that is the case, Sec.36.305(c) requires the cinema to establish a film rotation schedule that provides reasonable access for individuals who use wheelchairs to films being presented by the cinema.
A critical determination is what constitutes an effective auxiliary aid or service. The Department’s proposed rule recommended that, in determining what auxiliary aid to use, the public accommodation consult with an individual before providing him or her with a particular auxiliary aid or service. Many persons with disabilities, particularly persons who are deaf or hard of hearing, recommended that the rule should require that public accommodations give "primary consideration’’ to the "expressed choice’’ of an individual with a disability.
No, latch clearance 12″ minimum is required for forward approaches onthe push-side of doors equipped with both a closer and a latch. If adoor has a closer but no latch, or a latch and no closer, no additionallatch side clearance is required (although providing the clearance ishelpful in maneuvering through doors with closers without latches). Thisis also true for the additional depth required for hinge approaches onthe push side when both a closer and latch is provided.
Applying the general requirements for alterations to housing can result in partially accessible dwelling units where single elements or spaces in dwelling units are altered. The 1991 Standards require areas of rescue assistance or horizontal exits in facilities with levels above or below the level of exit discharge. Areas of rescue assistance are spaces that have direct access to an exit, stair, or enclosure where individuals who are unable to use stairs can go to call for assistance and wait for evacuation. The 2010 Standards incorporate the requirements established by the IBC.
Many dimensions in the ADA Standards are expressed as a range instead ofan absolute so that designers can allow some room for minor deviationsin construction or manufacturing. For title III of the ADA, the 2010 Standards consist of both theregulatory provisions in 28 CFR part 36, subpart D, and appropriatesections of the Access Board’s 2004 ADA Accessibility Guidelines (36 CFRpart 1191, appendices B and D). As implemented under title II, the 2010 Standards consist of theregulatory provisions in 28 CFR §35.151 and appropriate sections of theAccess Board’s 2004 ADA Accessibility Guidelines (36 CFR part 1191,appendices B and D). The clear width is measured from the stop to the face ofdoors or gates open 90⁰ (or to the leading edge of sliding or foldingdoors. No projection into the clear width is permitted below 34″. New provisions of the Standards at sections 230.1 and 708 require two-way communications systems to be equipped with visible as well as audible signals.
It is noted, however, that the existence of this language in the advisory does not require a place of transient lodging that does not offer smoking guest rooms at its facility to do so only for individuals with disabilities. Section 707 of the Standards adds specific technical requirements for speech output, privacy, tactilely-discernible input controls, display screens, and Braille instructions to the general accessibility requirements set out in the 1991 Standards. Machines shall be speech enabled and exceptions are provided that cover when audible tones are permitted, when advertisements or similar information are provided, and where speech synthesis cannot be supported. The 1991 Standards require these machines to be accessible to and independently usable by persons with visual impairments, but do not contain any technical specifications.
Shelves shall be located 40 inches (1015 mm) minimum and 48 inches (1220 mm) maximum above the finish floor. The purpose of requiring the drinking fountain spout to produce a flow of water 4 inches (100 mm) high minimum is so that a cup can be inserted under the flow of water to provide a drink of water for an individual who, because of a disability, would otherwise be incapable of using the drinking fountain. The spout shall be located 15 inches (380 mm) minimum from the vertical support and 5 inches (125 mm) maximum from the front edge of the unit, including bumpers.


No comments:
Post a Comment